As promised, this week’s column looks at the importance of tax rates in the overall scheme of tax policy in any country. I start by saying that lower rates of tax do matter – they allow the taxpayer to retain a higher level of the income earned which they can use for re-investment or higher dividend payments to shareholders. They can also make a country more competitive since prospective investors pay some attention to countries’ nominal tax rates in their investment equation. Hence, the decision to reduce the corporate tax rates by five percentage points would be welcomed both by companies and individuals, as evidenced by the swift response of the Private Sector Commission (PSC) to the announcement by the Minister of Finance.
 In making his announcement the Minister said companies benefiting from this measure would be in a position to retain and invest a significantly higher share of their profits. While some may suggest that the reduction in the tax rate had an unmistakable eye on the upcoming general elections, they cannot argue with the effect advanced by the Minister since by definition a reduced tax charge leaves more after-tax profits which are available for investments, higher dividend payments and related party loans. But seemingly too quick to please the political directorate, it was the private sector representatives who stated that the reduction would make Guyana competitive in terms of tax rates.
In making his announcement the Minister said companies benefiting from this measure would be in a position to retain and invest a significantly higher share of their profits. While some may suggest that the reduction in the tax rate had an unmistakable eye on the upcoming general elections, they cannot argue with the effect advanced by the Minister since by definition a reduced tax charge leaves more after-tax profits which are available for investments, higher dividend payments and related party loans. But seemingly too quick to please the political directorate, it was the private sector representatives who stated that the reduction would make Guyana competitive in terms of tax rates.
The private sector leaders travel around and must know that the corporate rate in two of our major Caricom trading partners (Trinidad and Tobago and Barbados) is 25% while our reduced rates are 30% for non-commercial companies, 40% for commercial companies and 45% for telephone companies. Non-regional investors on the other hand would be familiar with much lower tax rates in their own countries, so that our 30%/40% would still sound to them extremely high.
The biggest but unacknowledged problem for the private sector is the failure by this government to address tax policy and tax reform which it has been promising for eighteen years. For example, tax policy would address how we treat one sector over another, whether a single person should receive the same personal allowance as the single parent with a number of children, whether there should be differentials in tax rates, the balance between direct and indirect taxes, extending the use of the withholding tax to domestic contractors, etc. Unfortunately what passes for tax policy is the demand for tax revenues to finance a bloated, politicised and inefficient bureaucracy and a government that seems to have an insatiable appetite to spend, spend and spend.
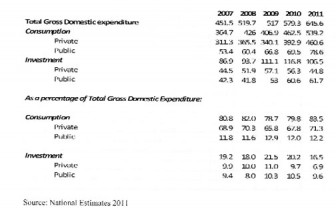
I strongly believe that the flat, across-the-board reduction of five percentage points is both intellectually lazy and politically cowardly. If the officials of the Ministry of Finance were to read the report of the Bank of Guyana (latest mid-year 2010) or indeed the statistics in their own National Estimates, they would see that the business community is increasingly investment-averse despite all the tax and contracts goodies thrown their way. As the following table shows, growth in the economy is being driven by the public sector.
Goodies
The tax laws are now replete with all forms of incentives, some of which are general and others specific, some found in legislation and others in agreements signed by the political arm of the government. Some are intended to encourage exports (the export allowance), investments (the Income Tax in Aid of Industry) which also provides tax holidays for investments in the hinterland, low cost housing and exemption from VAT.
More than a decade after its introduction and generous exemptions for public companies investments, the Stock Exchange remains extremely inactive with no new issuers, ie, companies going public, or existing companies offering new issues. In the absence of rules on thin capitalisation and the differential tax treatment of loans versus dividends, even our larger public companies find it cheaper to borrow than to raise new capital. There was a time when Banks DIH and DDL could be relied upon to make rights issue or bonus shares which allowed for some greater liquidity in the market. They have not needed to do so.
The commercial banks hold deposits of more than $230 billion dollars of which loans and advances, inclusive of the public sector loans, amounted to $68.9 billion. For several years the government has been critical of the commercial banks and Minister Manzoor Nadir, the self-appointed chief spokesperson of the 2011 Budget is on record as stating that “the commercial banks have been penalizing our people for too long.” He is also on record for cautioning against differential tax rates to protect the locally manufactured products since they “protect local inefficiencies.” That Mr Nadir now supports the things he had earlier railed against shows how politicised the tax system is, how it is influenced by the changing tides of political opportunitism and why we have a tax system that is, by any measure other than revenue collection, so dysfunctional.
Drivers
Tax policy has to be driven by a vision and relevant information. This column has called for more relevant information to be disclosed in public documents. Principal among these would be the annual report of the Guyana Revenue Authority which the Minister of Finance has failed to table in the National Assembly for some time now. Let us see how much the construction sector, the bauxite sector, the forestry sector, the agriculture sector including rice, sugar and other crops sectors contribute to the national coffers, and how much remissions, rebates and holidays they receive which may amount to billions each year. And yes, we should be able to see how much each region contributes and compare this with their receipts from the central government.
The Minister has access to data that would tell him that the bulk of the corporate taxes collected by the GRA is paid literally by a handful of companies. These are the commercial banks, Banks DIH and DDL, GT&T and Digicel and the oil distribution companies. The majority of companies could not care about tax rate – they decide how much tax they will pay and have their accounts prepared accordingly. This of course is also true of the self-employed, for which Regent Street is a metonym and to which political protest is as applicable as tax evasion is. There is a strong suspicion that setting a payment level for any period is also true of VAT, and as I have written before in this column, that some politicians have given pledges to the business community for tax support in exchange for votes.
Conclusion
Tax policy and tax reform will clearly have to wait for some years. The Jagdeo-Singh duo is comfortable with the status quo under which urban workers and consumers are the biggest contributors. They are equally comfortable with some sectors and segments making no contribution to the national coffers while demanding so much. The parliamentary debate on the 2011 Budget will close without any discussion on either tax policy or tax reform. In that sense, we are all losers.