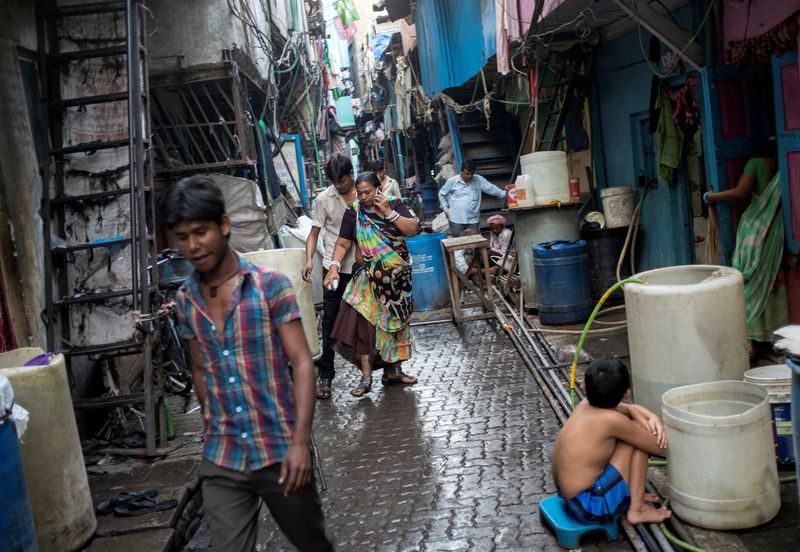
NEW DELHI, (Reuters) – Nearly 135 million people, around 10% of India’s population, escaped poverty in the five years to March 2021, a government report found today.
Rural areas saw the strongest fall in poverty, according to the study, which used the United Nations’ Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI), based on 12 indicators such as malnutrition, education and sanitation. If people are deprived in three or more areas, they are identified as “MPI poor.”
“Improvements in nutrition, years of schooling, sanitation and cooking fuel played a significant role in bringing down poverty,” said Suman Bery, vice-chairman of the NITI Aayog, the government think-tank that released the report.
The percentage of the population living in poverty fell to 15% in 2019-21 from 25% in 2015/16, according to the report, which was based on the 2019-21 National Family Health Survey.
A report by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) released last week said the number of people living in multidimensional poverty fell to 16.4% of India’s population in 2021 from 55% in 2005.
According to UNDP estimates, the number of people, who lived below the $2.15 per day poverty line had declined to 10% in India in 2021.
India’s federal government offers free food grain to about 800 million people, about 57% of country’s 1.4 billion population, while states spend billions of dollars on subsidising education, health, electricity and other services.
The state that saw the largest number moving out of poverty was Uttar Pradesh, with 343 million people, followed by the states of Bihar and Madhya Pradesh, according to the report.